简约且更新的 tsc --init
🌐 Minimal and Updated tsc --init
一段时间以来,TypeScript 编译器支持一个 --init 标志,可以在当前目录中创建一个 tsconfig.json。
在过去的几年里,运行 tsc --init 会创建一个非常“完整”的 tsconfig.json,其中填充了被注释掉的设置及其说明。
我们的设计初衷是让选项易于发现并方便切换。
🌐 For a while, the TypeScript compiler has supported an --init flag that can create a tsconfig.json within the current directory.
In the last few years, running tsc --init created a very “full” tsconfig.json, filled with commented-out settings and their descriptions.
We designed this with the intent of making options discoverable and easy to toggle.
然而,结合外部反馈(以及我们自己的经验),我们发现人们通常会立即删除这些新的 tsconfig.json 文件中的大部分内容。 当用户想要发现新的选项时,我们发现他们依赖于编辑器的自动补齐功能,或者访问 我们网站上的 tsconfig 参考(生成的 tsconfig.json 就链接到这里!)。 每个设置的作用也在同一页面上有文档说明,并且可以通过编辑器的悬停/工具提示/快速信息查看。 虽然显示一些被注释掉的设置可能有帮助,但生成的 tsconfig.json 通常被认为是过度的。
🌐 However, given external feedback (and our own experience), we found it’s common to immediately delete most of the contents of these new tsconfig.json files.
When users want to discover new options, we find they rely on auto-complete from their editor, or navigate to the tsconfig reference on our website (which the generated tsconfig.json links to!).
What each setting does is also documented on that same page, and can be seen via editor hovers/tooltips/quick info.
While surfacing some commented-out settings might be helpful, the generated tsconfig.json was often considered overkill.
我们还觉得,现在是时候让 tsc --init 初始化时比我们目前启用的设置更多一些预设选项了。我们观察了一些用户在创建新 TypeScript 项目时常遇到的痛点和小问题。例如,大多数用户都是在模块中编写代码(而不是全局脚本),而 --moduleDetection 可以强制 TypeScript 将每个实现文件都当作模块处理。开发者通常也希望在运行时直接使用最新的 ECMAScript 特性,因此 --target 通常可以设置为 esnext。JSX 用户经常觉得回去设置 --jsx 是不必要的阻碍,并且其选项略显令人困惑。而且,项目通常会加载比 TypeScript 实际需要更多的 node_modules/@types 声明文件;但指定一个空的 types 数组可以帮助限制这个问题。
🌐 We also felt that it was time that tsc --init initialized with a few more prescriptive settings than we already enable.
We looked at some common pain points and papercuts users have when they create a new TypeScript project.
For example, most users write in modules (not global scripts), and --moduleDetection can force TypeScript to treat every implementation file as a module.
Developers also often want to use the latest ECMAScript features directly in their runtime, so --target can typically be set to esnext.
JSX users often find that going back to set --jsx is needless friction, and its options are slightly confusing.
And often, projects end up loading more declaration files from node_modules/@types than TypeScript actually needs; but specifying an empty types array can help limit this.
在 TypeScript 5.9 中,一个没有其他标志的普通 tsc --init 将生成以下 tsconfig.json:
🌐 In TypeScript 5.9, a plain tsc --init with no other flags will generate the following tsconfig.json:
json
🌐 For more details, see the implementing pull request and discussion issue.
支持 import defer
🌐 Support for import defer
TypeScript 5.9 引入了对 ECMAScript 延迟模块评估提案 的支持,使用新的 import defer 语法。这个功能允许你在导入模块时不立即执行该模块及其依赖,从而更好地控制工作和副作用的发生时间。
🌐 TypeScript 5.9 introduces support for ECMAScript’s deferred module evaluation proposal using the new import defer syntax.
This feature allows you to import a module without immediately executing the module and its dependencies, providing better control over when work and side-effects occur.
语法仅允许命名空间导入:
🌐 The syntax only permits namespace imports:
ts
import defer 的主要好处是模块只有在其某个导出首次被访问时才会被评估。
请看这个例子:
🌐 The key benefit of import defer is that the module is only evaluated when one of its exports is first accessed.
Consider this example:
ts
在使用 import defer 时,initializationWithSideEffects() 函数不会被调用,直到你实际访问导入命名空间的某个属性:
🌐 When using import defer, the initializationWithSideEffects() function will not be called until you actually access a property of the imported namespace:
ts
因为模块的求值会被延迟,直到你访问模块的某个成员,所以你不能对 import defer 使用具名导入或默认导入:
🌐 Because evaluation of the module is deferred until you access a member off of the module, you cannot use named imports or default imports with import defer:
ts
请注意,当你写 import defer 时,该模块及其依赖会被完全加载并准备执行。这意味着该模块必须存在,并且将从文件系统或网络资源中加载。常规 import 与 import defer 的主要区别在于,语句和声明的执行 会被延迟,直到你访问所导入命名空间的某个属性时才执行。
🌐 Note that when you write import defer, the module and its dependencies are fully loaded and ready for execution.
That means that the module will need to exist, and will be loaded from the file system or a network resource.
The key difference between a regular import and import defer is that the execution of statements and declarations is deferred until you access a property of the imported namespace.
此功能对于有条件加载具有高成本或特定平台初始化的模块特别有用。它还可以通过延迟模块评估直到实际需要应用功能时,提高启动性能。
🌐 This feature is particularly useful for conditionally loading modules with expensive or platform-specific initialization. It can also improve startup performance by deferring module evaluation for app features until they are actually needed.
请注意,import defer 完全不会被 TypeScript 转换或“降级”。它旨在用于原生支持该特性的运行时,或由可以应用适当转换的工具(例如打包器)使用。这意味着 import defer 仅在 --module 模式下的 preserve 和 esnext 中才能工作。
🌐 Note that import defer is not transformed or “downleveled” at all by TypeScript.
It is intended to be used in runtimes that support the feature natively, or by tools such as bundlers that can apply the appropriate transformation.
That means that import defer will only work under the --module modes preserve and esnext.
我们要感谢 Nicolò Ribaudo,他在 TC39 中支持了这一提案,并且还提供了该功能的实现。
🌐 We’d like to extend our thanks to Nicolò Ribaudo who championed the proposal in TC39 and also provided the implementation for this feature.
支持 --module node20
🌐 Support for --module node20
TypeScript 为 --module 和 --moduleResolution 设置提供了几种 node* 选项。最近,--module nodenext 已经支持从 CommonJS 模块 require() ECMAScript 模块的能力,并且正确地拒绝导入断言(转而使用符合标准的 import attributes)。
🌐 TypeScript provides several node* options for the --module and --moduleResolution settings.
Most recently, --module nodenext has supported the ability to require() ECMAScript modules from CommonJS modules, and correctly rejects import assertions (in favor of the standards-bound import attributes).
TypeScript 5.9 为这些设置提供了一个稳定选项,称为 node20,旨在模拟 Node.js v20 的行为。该选项未来不太可能出现新行为,这与 --module nodenext 或 --moduleResolution nodenext 不同。同样,不像 nodenext,指定 --module node20 将意味着 --target es2023,除非另行配置。另一方面,--module nodenext 则意味着浮动的 --target esnext。
🌐 TypeScript 5.9 brings a stable option for these settings called node20, intended to model the behavior of Node.js v20.
This option is unlikely to have new behaviors in the future, unlike --module nodenext or --moduleResolution nodenext.
Also unlike nodenext, specifying --module node20 will imply --target es2023 unless otherwise configured.
--module nodenext, on the other hand, implies the floating --target esnext.
欲了解更多信息,请查看此处的实现。
🌐 For more information, take a look at the implementation here.
DOM API 中的摘要描述
🌐 Summary Descriptions in DOM APIs
以前,TypeScript 中的许多 DOM API 仅链接到该 API 的 MDN 文档。这些链接虽然有用,但并没有提供 API 功能的快速总结。感谢 Adam Naji 的一些改动,TypeScript 现在为许多 DOM API 提供了基于 MDN 文档的摘要描述。你可以在 这里 和 这里 查看更多这些更改。
🌐 Previously, many of the DOM APIs in TypeScript only linked to the MDN documentation for the API. These links were useful, but they didn’t provide a quick summary of what the API does. Thanks to a few changes from Adam Naji, TypeScript now includes summary descriptions for many DOM APIs based on the MDN documentation. You can see more of these changes here and here.
可展开的悬停效果(预览版)
🌐 Expandable Hovers (Preview)
快速信息(也称为“编辑器提示”和“悬停提示”)对于查看变量的类型或类型别名实际指向的内容非常有用。
不过,人们通常希望更深入,获取快速信息提示中显示内容的详细信息。
例如,如果我们将鼠标悬停在以下示例中的参数 options 上:
ts
我们只剩下 (parameter) options: Options。
🌐 We’re left with (parameter) options: Options.
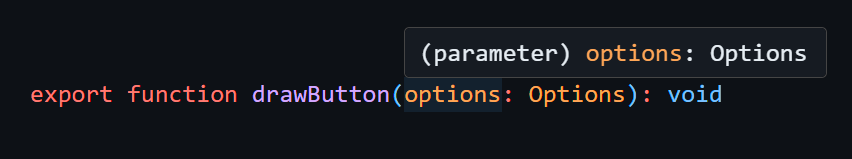
我们真的需要跳到类型 Options 的定义去查看这个值有哪些成员吗?
🌐 Do we really need to jump to the definition of the type Options just to see what members this value has?
以前,情况确实是这样的。
为了帮助这里,TypeScript 5.9 现在正在预览一个名为可扩展悬停的功能,或者称为“快速信息详细程度”。
如果你使用像 VS Code 这样的编辑器,现在你会在这些悬停提示的左侧看到 + 和 - 按钮。
点击 + 按钮可以更深入地展开类型,而点击 - 按钮则会收缩回上一次的视图。
🌐 Previously, that was actually the case.
To help here, TypeScript 5.9 is now previewing a feature called expandable hovers, or “quick info verbosity”.
If you use an editor like VS Code, you’ll now see a + and - button on the left of these hover tooltips.
Clicking on the + button will expand out types more deeply, while clicking on the - button will collapse to the last view.
此功能当前处于预览阶段,我们正在寻求 TypeScript 及 Visual Studio Code 合作伙伴的反馈。更多详情,请参见此功能的 PR。
🌐 This feature is currently in preview, and we are seeking feedback for both TypeScript and our partners on Visual Studio Code. For more details, see the PR for this feature here.
可配置的最大悬停长度
🌐 Configurable Maximum Hover Length
有时,快速信息提示可能会变得非常长,以至于 TypeScript 会截断它们以提高可读性。问题是,经常最重要的信息会被省略在悬停提示之外,这会让人感到沮丧。为了解决这个问题,TypeScript 5.9 的语言服务器支持可配置的悬停长度,可以在 VS Code 中通过 js/ts.hover.maximumLength 设置进行配置。
🌐 Occasionally, quick info tooltips can become so long that TypeScript will truncate them to make them more readable.
The downside here is that often the most important information will be omitted from the hover tooltip, which can be frustrating.
To help with this, TypeScript 5.9’s language server supports a configurable hover length, which can be configured in VS Code via the js/ts.hover.maximumLength setting.
此外,新的默认悬停长度比以前的默认值大得多。这意味着在 TypeScript 5.9 中,你默认应该会在悬停提示中看到更多信息。更多详情,请参阅 此功能的 PR 以及 Visual Studio Code 的相应更改。
🌐 Additionally, the new default hover length is substantially larger than the previous default. This means that in TypeScript 5.9, you should see more information in your hover tooltips by default. For more details, see the PR for this feature here and the corresponding change to Visual Studio Code here.
优化
🌐 Optimizations
缓存映射器实例化
🌐 Cache Instantiations on Mappers
当 TypeScript 用特定类型参数替换类型参数时,它可能会反复生成许多相同的中间类型。在像 Zod 和 tRPC 这样的复杂库中,这可能导致性能问题以及因类型实例化深度过大而报告的错误。多亏了 Mateusz Burzyński 的 一个更改,TypeScript 5.9 在对某个特定类型实例化开始工作后,能够缓存许多中间实例化结果。这反过来避免了大量不必要的工作和内存分配。
🌐 When TypeScript replaces type parameters with specific type arguments, it can end up instantiating many of the same intermediate types over and over again. In complex libraries like Zod and tRPC, this could lead to both performance issues and errors reported around excessive type instantiation depth. Thanks to a change from Mateusz Burzyński, TypeScript 5.9 is able to cache many intermediate instantiations when work has already begun on a specific type instantiation. This in turn avoids lots of unnecessary work and allocations.
避免在 fileOrDirectoryExistsUsingSource 中创建闭包
🌐 Avoiding Closure Creation in fileOrDirectoryExistsUsingSource
在 JavaScript 中,即使封装函数只是将参数传递给另一个没有捕获变量的函数,函数表达式通常也会分配一个新的函数对象。在围绕文件存在性检查的代码路径中,Vincent Bailly 发现了这些传递函数调用的示例,尽管底层函数只接受单个参数。考虑到在大型项目中可能进行的存在性检查次数,他引用了大约 11% 的加速。 在这里查看更多关于此更改的信息。
🌐 In JavaScript, a function expression will typically allocate a new function object, even if the wrapper function is just passing through arguments to another function with no captured variables. In code paths around file existence checks, Vincent Bailly found examples of these pass-through function calls, even though the underlying functions only took single arguments. Given the number of existence checks that could take place in larger projects, he cited a speed-up of around 11%. See more on this change here.
值得注意的行为变更
🌐 Notable Behavioral Changes
lib.d.ts 变更
🌐 lib.d.ts Changes
为 DOM 生成的类型可能会对代码库的类型检查产生影响。
🌐 Types generated for the DOM may have an impact on type-checking your codebase.
此外,一个显著的变化是 ArrayBuffer 已被修改,因此它不再是多个不同 TypedArray 类型的超类型。这也包括 UInt8Array 的子类型,例如来自 Node.js 的 Buffer。
因此,你会看到新的错误信息,例如:
🌐 Additionally, one notable change is that ArrayBuffer has been changed in such a way that it is no longer a supertype of several different TypedArray types.
This also includes subtypes of UInt8Array, such as Buffer from Node.js.
As a result, you’ll see new error messages such as:
如果你在使用 Buffer 时遇到问题,你可能首先需要检查自己是否正在使用最新版本的 @types/node 包。这可能包括运行
🌐 If you encounter issues with Buffer, you may first want to check that you are using the latest version of the @types/node package.
This might include running
大多数情况下,解决方法是指定一个更具体的底层缓冲区类型,而不是使用默认的 ArrayBufferLike(即明确写出 Uint8Array<ArrayBuffer> 而不是单纯的 Uint8Array)。
在某些情况下,当一些 TypedArray(如 Uint8Array)被传递给期望 ArrayBuffer 或 SharedArrayBuffer 的函数时,你也可以尝试访问该 TypedArray 的 buffer 属性,如以下示例所示:
🌐 Much of the time, the solution is to specify a more specific underlying buffer type instead of using the default ArrayBufferLike (i.e. explicitly writing out Uint8Array<ArrayBuffer> rather than a plain Uint8Array).
In instances where some TypedArray (like Uint8Array) is passed to a function expecting an ArrayBuffer or SharedArrayBuffer, you can also try accessing the buffer property of that TypedArray like in the following example:
diff
类型参数推断变更
🌐 Type Argument Inference Changes
为了修复推断过程中类型变量的“泄漏”,TypeScript 5.9 可能会对类型引入更改,并可能在某些代码库中产生新的错误。这些变化难以预测,但通常可以通过在泛型函数调用中添加类型参数来修复。在这里查看更多详情。
🌐 In an effort to fix “leaks” of type variables during inference, TypeScript 5.9 may introduce changes in types and possibly new errors in some codebases. These are hard to predict, but can often be fixed by adding type arguments to generic functions calls. See more details here.